If you’re getting started with DIY electronics or Arduino projects, you’ve probably heard of a breadboard. It’s one of the most essential tools for prototyping electronic circuits without any soldering. In this guide, you’ll learn what a breadboard is, how it works, and how to use it step by step for your next project.
What is a Breadboard?
A breadboard is a plastic board with a grid of tiny holes where you can insert electronic components and wires. It allows you to connect circuits temporarily without soldering, making it perfect for learning, experimenting, or prototyping.
Inside, the holes are connected by metal strips that create an electrical path. These strips are organized in rows and columns so you can easily connect resistors, LEDs, transistors, sensors, and other components.
💡 Quick Tip: Breadboards come in different sizes like mini, half-size, and full-size. Beginners often start with a half-size breadboard.
How Does a Breadboard Work?
A breadboard is divided into three main sections:
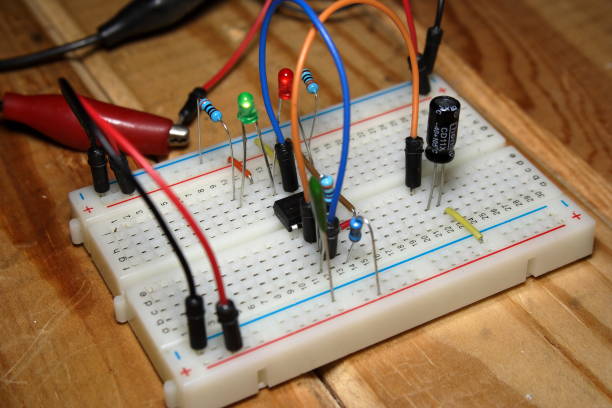
- Power Rails – The two long strips on each side, usually marked with red (+) and blue (-) lines. They distribute power from your battery or power supply.
- Terminal Strips – The middle section where you connect most of your components. Each vertical column (usually 5 holes) is electrically connected.
- Gap or Channel – The center divider separates both sides of the breadboard, allowing space to place integrated circuits (ICs).
When you insert component leads and jumper wires into connected holes, they complete a circuit path — enabling current to flow.
How to Use a Breadboard (Step-by-Step)
Let’s go through a simple example — lighting up an LED with a resistor.
🪛 You’ll Need:
- 1 × Breadboard
- 1 × LED
- 1 × 220Ω resistor
- Jumper wires
- 5V power source (like from an Arduino board)
👉 Buy a beginner-friendly breadboard kit on Amazon(Affiliate Link)
Steps:
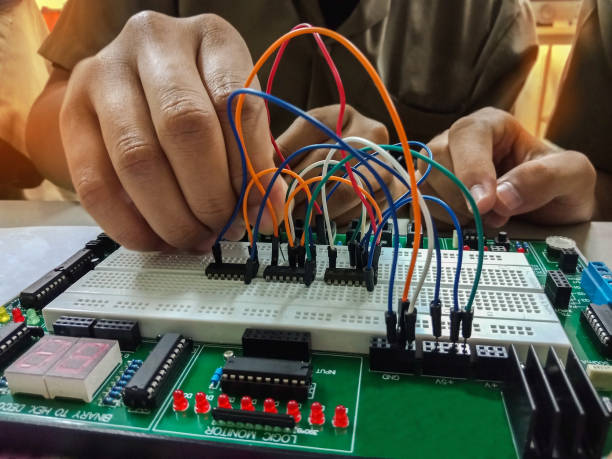
- Connect Power:
Attach the 5V pin from your Arduino (or power supply) to the red (+) rail and the GND pin to the blue (-) rail. - Insert the LED:
Place the LED on the terminal strip — remember, the long leg (anode) is positive and the short leg (cathode) is negative. - Add the Resistor:
Connect one end of the resistor to the LED’s cathode (short leg) and the other end to the GND rail. This prevents your LED from burning out. - Complete the Circuit:
Use a jumper wire to connect the 5V rail to the LED’s anode (long leg). The LED should light up!
Tools You’ll Need
To make your breadboard projects smoother, here are some must-have tools:
- Jumper wire kit – Get on Amazon → (Affiliate link)
- Resistor and LED pack – Buy here → (Affiliate link)
- Arduino starter kit – Check this kit → (Affiliate link)
- Multimeter – Recommended model → (Affiliate link)
💬 Related Post: How to Use a Multimeter Step by Step
Tips for Using a Breadboard
- Always check connections before powering up.
- Use color-coded jumper wires (red for +, black for -).
- Don’t force components; gentle pressure is enough.
- Label your power rails if you’re using multiple voltages.
- Keep your setup clean and organized for easy troubleshooting.
Applications of a Breadboard
Breadboards are perfect for:
- Learning electronics
- Prototyping Arduino projects
- Testing sensors and circuits
- DIY experiments
- STEM education for students
If you’re experimenting with IoT projects, breadboards make it simple to test sensors like DHT11, Ultrasonic sensors, or IR modules before soldering them permanently.
💬 Read Next: ESP32 vs Arduino: Which One Should You Buy?
Conclusion
A breadboard is the heart of every beginner electronics setup. It helps you test circuits quickly, avoid soldering mistakes, and understand how components interact. Once you master it, you can easily move on to building permanent PCB-based projects.
So, grab a breadboard kit and start your DIY journey today — the best way to learn electronics is by experimenting!