If you have ever experienced one of the situations listed in the opening paragraph, you are definitely not the only one. The fingerprint of ESP32 is its strength, but at the same time, it is its weakness too. The ESP32 has more than 30 GPIOs, different comm. protocols, plus designated boot or flash function pins; thus, the developers who are not very experienced can also get lost in its flexibility.
However, if you ask me the question, what is the good news? I will tell you the answer, it is the understanding of the ESP32 pinout that makes everything work together perfectly. Your circuit design will become more reliable, debugging will be faster, and you will be able to use advanced features like touch sensors, DACs, and deep sleep.
We will present the ESP32 pinout in a very simple and practical way in this comprehensive guide, going well past the basic diagrams. Whether you are a novice putting together your first IoT project or a technician fine-tuning a production design, reading this article will make you feel confident about your mastery of the ESP32 pinout.
🧩 What is ESP32?
The ESP32 is an inexpensive and low-power microcontroller created by Espressif Systems, and it has the following characteristics:
- Dual-core 32-bit CPU (maximum frequency of 240 MHz)
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth integrated
- Support for various peripherals
- Pin multiplexing that is adjustable
As per the statement of Espressif, the yearly shipment of the ESP32 chips reaches millions which are basically Ic chips sourcing with one of the highest IoT applications worldwide.
The unique feature of ESP32 is its pinout that allows most of the pins to be under multiplexing. So, one pin can function as multiple like GPIO, SPI, I2C, ADC, PWM, etc. depending on your setup.
💡 Recommended Board: Buy ESP32 Development Board on Amazon(affiliate link)
🔍 ESP32 Pinout Overview
The various ESP32 development boards (for instance, ESP32-WROOM-32, ESP32-DevKit V1, or NodeMCU-32S) are differing in the pin arrangement somewhat, but they are still able to carry out the same functions for the most part.
Here’s a general ESP32 pinout diagram:
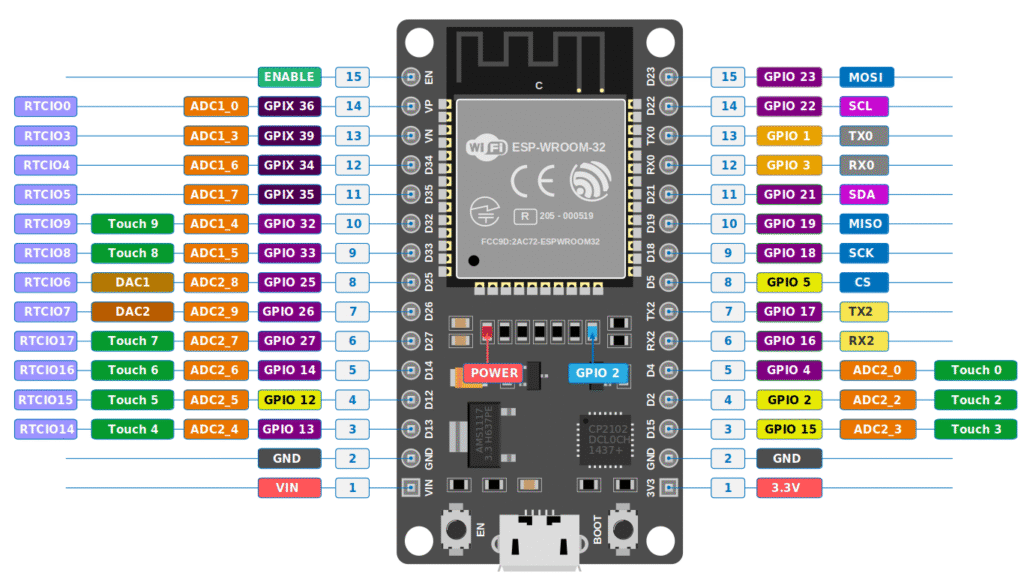
⚡ ESP32 Pin Categories Explained
Let’s break down the ESP32 pins into categories for better understanding.
1. Power Pins
- 3V3: Provides 3.3V output.
- VIN (5V): Power input when connected via USB or external power source.
- GND: Ground pins.
⚙️ Use a reliable breadboard power supply like this one on Amazon to ensure stable power for your ESP32 projects. (affiliate link)
2. GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) Pins
The ESP32 has 30+ GPIO pins that can be used for input or output.
However, not all pins are created equal — some are better for digital I/O, while others are reserved for
specific tasks.
| Pin | Default Function | Recommended Use |
|---|---|---|
| GPIO0 | Boot mode selector | Avoid using |
| GPIO2 | Default output | Safe for use |
| GPIO4, 5, 18, 19 | SPI interface | Use for sensors/modules |
| GPIO12-15 | HSPI interface | Use with caution |
| GPIO34-39 | Input only | Sensors (no output allowed) |
Tip: Always check the ESP32 datasheet before assigning pins to avoid boot issues.
3. ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) Pins
ESP32 comes with 18 ADC channels (ADC1 and ADC2) allowing it to read analog voltages from sensors like potentiometers, temperature sensors, or light sensors.
- ADC1: GPIO32–GPIO39
- ADC2: GPIO0, GPIO2, GPIO4, GPIO12–GPIO15, GPIO25–GPIO27
⚡ Check out our guide — How to Use ESP32
4. DAC (Digital to Analog Converter) Pins
The ESP32 has two DAC channels (GPIO25 and GPIO26).
These are used to generate analog output signals, such as for LED fading or audio output.
5. Touch Pins
ESP32 supports 10 touch-sensitive pins (T0–T9).
These can detect changes in capacitance — useful for touch buttons or proximity sensors.
6. PWM Pins
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is available on almost all GPIO pins.
You can use it for controlling LED brightness, motor speed, or servo angle.
Affiliate link: Buy a Servo Motor Kit on Amazon
7. Communication Pins
| Protocol | Pins Used | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| UART | GPIO1 (TX), GPIO3 (RX) | Serial Communication |
| SPI | GPIO23 (MOSI), GPIO19 (MISO), GPIO18 (SCK), GPIO5 (CS) | Sensors & Displays |
| I2C | GPIO21 (SDA), GPIO22 (SCL) | Modules like OLED, MPU6050 |
⚙️ Boot & Flash Pins
Certain pins play a critical role during boot or programming:
- GPIO0: Must be LOW to enter bootloader mode.
- EN (Enable): Resets the chip when pulled LOW.
Tips for Using ESP32 Pins

- Avoid using GPIO6–GPIO11 (used for SPI flash).
- Use GPIO34–39 for sensor input only.
- Always use 3.3V logic sensors — higher voltage can damage the board.
- Use breadboard-friendly ESP32 boards like the NodeMCU-32S for easy prototyping.
Recommended Tools for ESP32 Projects
- ESP32 Development Board – Buy Now on Amazon
- Breadboard + Jumper Wires – Buy Combo Kit
- Soldering Kit – Best Soldering Kit for Beginners (internal)
Conclusion
The ESP32 pinout is highly versatile and can handle multiple functions simultaneously. Whether you’re building a Wi-Fi robot, IoT home automation system, or a DIY sensor module, understanding the pin configuration is the first step toward successful projects.
Explore more tutorials on our website for ESP32 projects, sensor interfacing, and IoT ideas to level up your electronics skills!